

Coastlines for kids
Coastlines for kids learning in KS2 at Primary School. Homework help with coastlines and coastal erosion. Discover coastlines their features and what causes coastal erosion.
What are coasts?
Coasts are where the land meets the sea. They are some of the most exciting places on Earth because they are always changing. The constant movement of waves, tides, and wind shapes the land in different ways, making coastlines look very different from one another.
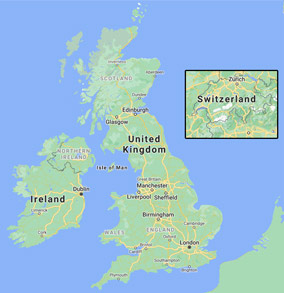
The United Kingdom has a very long coastline because it is an island completely surrounded by water. In fact, the UK has about 7,723 miles (12,429 km) of coastline—that’s long enough to stretch halfway around the world! Along these coasts you will find cliffs, sandy beaches, rocky bays, and winding estuaries.
Not every country has a coastline. For example, Switzerland is surrounded by other countries and has no access to the sea. A country without a coastline is called landlocked.
Types of coastline
There are two main types of coastlines, and the UK has both:
Rocky Coastlines - These have steep cliffs made of rock that rise up at the edge of the land. Some cliffs are made from hard rock like granite, which erodes very slowly, while others are made from softer rock like chalk, which wears away much faster. When the sea crashes into these cliffs, it can form caves, arches, stacks, and stumps—amazing natural features you can see along places like the Jurassic Coast in Dorset.
Coastal Plains - These are flatter areas where the land gently slopes down to meet the sea. Coastal plains often have sand dunes, mudflats, and salt marshes. Because they are low-lying, they are the first places to flood during storms or when sea levels rise. A good example in the UK is Northumberland, where wide sandy beaches stretch for miles.

Coastal features
Coasts are full of interesting features that are shaped by the sea, wind, and weather over thousands of years. Some common coastal features include:
Headlands and bays
Headlands are areas of hard rock that stick out into the sea, while bays are the softer, eroded areas between them. Waves erode the softer rock faster, creating these curved shapes along the coastline.
Cliffs
Cliffs are steep faces of rock that rise sharply from the shore. They are formed when waves and weather slowly wear away the base of the rock. Over time, parts of the cliff can collapse, creating new shapes.
Caves, arches, and stacks
These features often form on headlands. Waves carve out caves in the rock, which can grow into arches. When the arch collapses, it leaves a stack, a tall pillar of rock standing in the sea.
Beaches
Beaches are made of sand, pebbles, or shingle and are created when waves deposit sediment along the coast. The type of material on a beach depends on the type of rocks nearby and the strength of the waves.
Sand dunes
Sand dunes are hills of sand formed by the wind blowing sand from the beach inland. They help protect the coast from flooding and provide habitats for plants and animals.
Estuaries and mudflats
Estuaries are areas where rivers meet the sea, and mudflats form in these calm waters when fine sediment settles. These are important habitats for birds and other wildlife.
How are beaches formed?
Beaches are some of the most popular parts of the coast, but they take a long time to form. They are created by the action of waves, tides, and erosion (the wearing away of rocks).
It usually begins when waves crash against cliffs or rocky shorelines. The force of the water loosens large rocks, which fall into the sea. Once in the water, the rocks are rolled, tumbled, and smashed together by the movement of the waves. Over time, the rocks are broken down into smaller and smaller pieces until they eventually turn into smooth pebbles or tiny grains of sand.
The sea doesn’t just break down rocks—it also moves them around. As the tides rise and fall, the waves carry sand, pebbles, and shells towards the shore and deposit them. Over many years, these materials build up to create a beach.
- Some beaches are made of soft golden sand, where the rocks have been broken down into very fine grains.
- Other beaches are covered in pebbles or shingle, which happens when the waves are not strong enough or haven’t had enough time to grind the rocks down into sand.
- In tropical places, beaches can even be made from tiny pieces of coral or shells that have been broken apart.
The shape and size of a beach depend on lots of factors
- Wave strength – Strong, crashing waves often wash material away, leaving behind pebbles, while gentle waves allow sand to settle.
- Type of rock – Hard rocks like granite take much longer to wear down, so beaches near them may be rocky, while softer rocks like sandstone create sandy beaches.
- Ocean floor slope – Shallow slopes usually create wide sandy beaches, while steep slopes form narrower, pebble-filled beaches.
- Rivers and streams – Sometimes beaches are also formed when rivers carry sediment (bits of rock, mud, and sand) into the sea, where the waves spread it along the coast.
What causes tides?
Tides happen every day. Have you ever been to a beach and noticed the water slowly creeping up the shore, making the beach smaller? Or seen the water retreating back into the sea? These regular rising and falling of the sea are called tides, and they happen because of the gravitational pull of the Moon and the Sun.
The Moon’s gravity pulls on the water in the oceans. This pull creates a bulge of water on the side of the Earth facing the Moon. At the same time, there is another bulge on the opposite side of the Earth. These bulges of water move around as the Earth rotates, which is why the ocean level rises and falls, creating high tides and low tides.
The Sun also has a gravitational effect on the tides, although it is smaller than the Moon’s effect because it is much further away. When the Sun, Moon, and Earth are in a straight line, the Sun and Moon work together, creating especially high and low tides, called spring tides. When the Sun and Moon are at right angles to each other, they create smaller tides, called neap tides.
The height and timing of the tides also depend on:
- The shape of the coastline: Narrow bays can make tides higher.
- The depth of the water: Shallow water can cause tides to rise more dramatically.
- The Moon’s position: As the Moon moves around the Earth, the timing of high and low tides changes slightly each day.
Tides are important for marine life, fishing, and even sailing. They also help clean beaches and move nutrients and sand along the coast.
How are cliffs formed?
Cliffs are steep faces of rock that rise up from the sea or land. They are formed over many years through the processes of erosion and weathering.
- Erosion happens when natural forces like waves, wind, and rain wear away the rock.
- Weathering is when rocks are slowly broken down by things like rainwater, freezing and thawing, or plant roots growing in cracks.
At the coast, the waves crash against the rocks and wear away the softer rocks more quickly than the harder rocks. This difference in strength creates some of the most dramatic shapes along the shoreline. For example:
- Sea caves form when waves hollow out soft rocks at the base of a cliff.
- Arches happen when the waves cut all the way through a section of rock, creating a bridge-like shape.
- Stacks are created when an arch collapses, leaving a tall, isolated column of rock standing in the sea.
Cliffs aren’t just found by the sea—they can also form on rivers and mountains where rock is worn away. Over thousands of years, cliffs slowly change shape, falling rocks and landslides adding new features to the coastline.
Famous cliffs in the UK
The UK has some amazing cliff formations that show how the sea and weather shape the land:
White Cliffs of Dover, England
These cliffs are famous for their bright white chalk and face the English Channel. They have stood as a symbol of Britain for centuries. Chalk is a soft rock. Over thousands of years, the waves and weather slowly wore away the softer rock, leaving tall, white cliffs facing the sea.
Jurassic Coast, Dorset & East Devon, England
This coastline has cliffs made of different types of rock, showing millions of years of Earth’s history. The softer rocks erode faster than the harder rocks, creating cliffs, coves, and small bays. Sometimes fossils get uncovered as the rock wears away!
Old Man of Hoy, Scotland
A tall sea stack off the coast of Orkney. It was formed when an arch collapsed. It rises 137 meters above the sea. Waves eroded the base of the cliffs, forming caves and arches. When an arch collapsed, it left the tall stack standing alone.
Flamborough Head, England
This area has high chalk cliffs with sea caves, arches, and stacks, making it a popular place for walkers and wildlife lovers. The cliffs here have been shaped by waves carving into the softer parts of the rock, forming caves and arches. Over time, some of these arches collapse, leaving stacks and cliffs with jagged edges.
Needles, Isle of Wight
Famous for its pointed chalk stacks sticking out of the sea, these cliffs are very dramatic and a popular tourist attraction. The chalk stacks used to be part of the main cliff. The sea slowly eroded the cliffs, forming arches, and when the arches fell, it left the pointed stacks sticking out of the water.
What is the impact of humans on the coastline?
Human activity can have both positive and negative effects on beaches and coastlines. People live, work, and play near the sea, but what we do can change the natural shape and health of the coast. Here are some ways humans impact coastlines:
Coastal development
Building houses, hotels, piers, jetties, and other structures can change the natural flow of water and sand along the coast. For example, seawalls and groynes can protect buildings from the sea, but they can also stop sand from moving naturally, which can cause erosion in other areas. This means some beaches might shrink or disappear over time.
Pollution
Littering and pollution are a big problem for coasts. Plastic waste, oil spills, and untreated sewage can harm plants, animals, and birds that live on beaches. Pollution can make beaches unsafe for swimming and ruin their natural beauty, making them less enjoyable for people too.
Beach grooming
Sometimes people change beaches to make them look nicer, such as raking, grading, or adding sand. While this can make beaches cleaner for visitors, it can disturb wildlife. Animals like crabs, birds, and turtles rely on the sand for nesting and shelter, so too much grooming can harm them.
Overuse
Busy beaches with lots of tourists and visitors can also be damaged. Walking over sand dunes, trampling plants, and leaving litter behind can weaken the sand and make the beach more prone to erosion. This also destroys habitats for animals that live on the beach.
Positive impacts
Not all human activity is harmful! People can also protect coastlines by planting vegetation on dunes, building safe pathways to prevent trampling, and cleaning up litter. Coastal management can help keep beaches beautiful and safe for both humans and wildlife.
Overall, it’s important to balance human use of the coast with nature’s needs. By protecting beaches and coastlines, we can make sure they stay healthy, safe, and beautiful for future generations.

What causes coastal erosion?
Coastal erosion in the UK happens when the land along the coast is worn away. It's a natural process, but it can be sped up by human activity and climate change. Understanding the causes helps communities protect the coastline and plan for the future. Over time, coastal erosion can change the shape of beaches, cliffs, and coastlines. Some of the main causes of coastal erosion include:
Wave action
Waves are one of the strongest forces shaping the coastline. In the UK, strong winds and storms can create huge waves that crash against cliffs and beaches, gradually wearing them away. Over many years, waves can create features like caves, arches, and stacks.
Climate change
Sea levels are rising around the world because of climate change. Higher sea levels mean that more land is at risk of being washed away by waves. Storms and high tides become even more damaging when the water reaches further inland, speeding up erosion.
Weathering
Weathering is when rocks break down slowly over time. The UK has many different rock types along the coast, some soft and some hard. Natural processes like:
- Freeze-thaw weathering (water gets into cracks in rocks, freezes, expands, and breaks the rock)
- Salt spray from the sea
- Rain and wind
These all weaken the rocks and make them more likely to be worn away by waves.
Human activity
People can also increase coastal erosion. Building houses, roads, and piers along the coast can change the natural flow of sand and water, making some areas more vulnerable. Dredging (removing sand or sediment from the sea for harbours) and other changes to the coastline can also increase erosion.
Combination of factors
Often, it is a combination of natural forces and human activity that causes the most erosion. For example, a soft cliff hit by storm waves and high tides is much more likely to collapse if human activities have weakened it further.

How can we stop coastal erosion?
Coastal erosion is a natural process that happens over time, and it cannot be completely stopped. However, people can use different methods to protect the most vulnerable parts of the coastline. Some common ways to prevent or slow down coastal erosion include:
Beach nourishment
This is when sand or other sediment is added to the beach to make it wider and deeper. A wider beach helps to push the sea further away from the coastline and reduces the impact of waves. The sand can come from dredging the sea nearby or from other areas. Beach nourishment is often used in places with popular beaches to protect homes, businesses, and tourism areas.
Coastal vegetation
Planting grasses, shrubs, and other plants helps to stabilize sand dunes and soil along the coast. The roots of the plants hold the sand in place, which reduces how much the wind and waves can move it. Coastal vegetation also provides habitats for animals like birds, crabs, and insects.
Hard structures
People sometimes build man-made structures to protect the coastline from waves:
- Seawalls: Large walls built along the coast to stop waves from hitting the land.
- Groynes: Wooden or stone barriers built perpendicular to the shore to trap sand and prevent it from washing away.
- Breakwaters: Offshore walls that reduce the strength of waves before they reach the coast.
While these structures can be effective, they are expensive and sometimes harm the environment by changing natural processes along the coast.
Move away from the area
In some places, it’s better to allow the coastline to erode naturally. This might happen if the erosion is too fast or if other methods won’t work. People living in these areas may need to relocate to safer places. This is called managed retreat and is often the cheapest and most sustainable solution in the long term.
Development restrictions
Governments can make rules to prevent building homes, roads, or other structures in areas that are at high risk of erosion. Limiting development in these areas helps reduce damage and risk to people while allowing nature to continue shaping the coastline naturally.










