Light & Sound
Year 5 & 6
Light & sound for Year 5 & 6 kids at Super Brainy Beans. Science homework help with how light helps us see things and how shadows can change. For children in Year 5 and 6, Key Stage 2 (KS2).
Pick a level
How light travels
Light appears to travel in straight lines. This idea helps scientists explain many things we see every day.
Because light travels in straight lines:
- Shadows are formed when an object blocks the light
- We cannot see around corners because light does not bend by itself
If light could curve around objects, we would be able to see things hidden behind them — but we can’t!

Seeing light travel
-
- Cut a very thin slit in a piece of card.
- Shine the torch through it in a darkened room.
- You should see a narrow beam of light showing a straight path.
- Now place a mirror in the path of the light. The beam will change direction.
- As you move the mirror the light will also change direction as it reflects.
This shows that light still travels in straight lines, but it can reflect (bounce) off shiny surfaces.
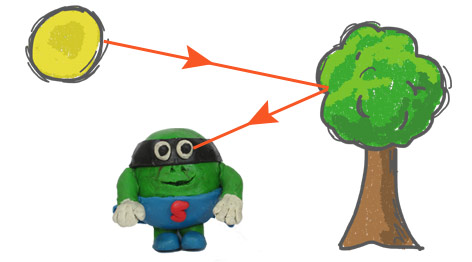
Seeing Objects
We can only see things when light enters our eyes. This happens in two main ways:
- Light travels directly from a light source (such as the Sun or a lamp) into our eyes
- Light travels from a light source, reflects off an object, and then enters our eyes
Most objects we see, like books, tables, and people, do not give off their own light. We see them because they reflect light from a light source.
 How does the eye detect light?
How does the eye detect light?Light travels in straight lines. When light hits an object, it is reflected (bounces off) and enters our eyes. This is how we see the object.
How shadows work
A shadow is formed when an object blocks light from a light source. Because light travels in straight lines and cannot bend around solid objects, the area behind the object does not receive any light. This creates a dark shape called a shadow.
Why shadows have the same shape
Shadows have the same outline (shape) as the object that makes them. This is because the light is blocked in straight lines, so the shadow copies the shape of the object facing the light source.
Even though a shadow may change in size, its shape stays the same. A circular object will always make a circular shadow, and a rectangular object will always make a rectangular shadow.
How the position of light affects shadows
The size of a shadow depends on where the light source is:
- When the object is close to the light source, the shadow is larger
- When the object is further away from the light source, the shadow is smaller
This happens because the light spreads out as it travels, changing how much of it is blocked.
Shadows and the time of day
The Sun acts like a moving light source during the day:
- In the morning and evening, the Sun is low in the sky, creating long shadows
- At midday, the Sun is high in the sky, creating short shadows
Even though the length and direction of shadows change, the shape always stays the same because light continues to travel in straight lines.

Testing shadows
- On a sunny day take some objects outside and lay them on a patio.
- With some chalk draw round each object's shadow.
- Come back at a differnet time of the day and draw new shadows.
- Compare the drawings, how they are different?
- What do you notice, longer or short shadows? What is the direction of the shadows? Are the shapes the same?
Reflection
Reflection happens when light bounces off a surface instead of passing through it. This is how we see our reflection in mirrors and shiny objects.
Some surfaces reflect light better than others:
- Mirrors reflect light very clearly
- Shiny, smooth surfaces reflect more light
- Rough or dull surfaces scatter light in many directions, making reflections unclear
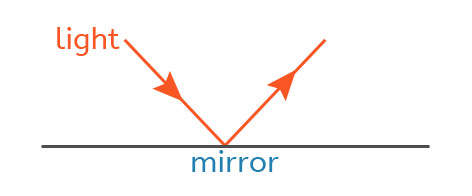
How light reflects
When light hits a mirror, it reflects in a very predictable way. The angle the light hits the mirror is the same as the angle it bounces away.
This rule is called the law of reflection. If you shine a torch at a mirror, you can see the light bounce off at the same angle on the other side.
Using Reflection in Everyday Life
Reflection is extremely useful:
- Mirrors allow us to see ourselves
- Periscopes use mirrors to help people see over or around objects
- Submarines use periscopes to see above the surface of the sea while staying underwater
In a periscope, light reflects off several mirrors and travels straight into the viewer’s eye.
 What is reflection?
What is reflection?When light from an object is reflected by a surface, it changes direction. It bounces off the surface at the same angle as it hits it.
Refraction
Refraction happens when light changes direction as it moves from one material to another, such as from air into water or air into glass.
This happens because light travels at different speeds in different materials.
Refraction explains why:
- a straw in a glass of water looks bent
- objects under water appear in a slightly different place
- rainbows form in the sky
Although light travels in straight lines, it bends when it enters water, making objects appear distorted
Rainbows
Sunlight is actually made up of many different colours. When sunlight passes through tiny drops of water in the air, the water:
- slows the light down
- bends it (refraction)
- splits it into colours
This creates a rainbow with red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo and violet.
Rainbows appear when:
- the Sun is behind you
- there is rain or mist in front of you

Double Rainbows
Sometimes we see double rainbows. This happens when light:
- reflects twice inside raindrops
- creates a second, fainter rainbow
- shows the colours in the reverse order
The second rainbow is always dimmer because less light reaches your eyes.
 Water rainbow
Water rainbow
- Shine a torch through a glass of water in a dark room.
- Twist the glass a little until you see a rainbow on the table or on the wall.
- On a sunny day, take the glass of water outside in the sunshine.
- Hold the glass over a piece of white paper and move it slowly until you see a rainbow.





 Water rainbow
Water rainbow