

Electricity
Year 5 & 6
Electricity Year 5 & 6 kids at Primary School KS2. Science homework help. Learn about voltage, cells, electrical circuits and symbols.
Pick a level
What is voltage?
 Voltage describes how much energy electricity has as it moves around a circuit. It tells us how powerful the electrical push is inside the wires.
Voltage describes how much energy electricity has as it moves around a circuit. It tells us how powerful the electrical push is inside the wires.
Circuits with different voltages can behave in different ways. A higher voltage can make electrical components work more strongly, while a lower voltage produces a weaker effect. This helps scientists explain why two circuits that look similar do not always work in the same way.
Voltage is measured in volts (V), but in primary school, the focus is on understanding what voltage means and how it affects a circuit, rather than measuring or calculating it.
Understanding voltage helps us predict what might happen when a circuit is changed.
The power of cells
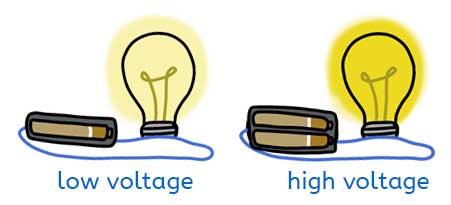 Cells (batteries) are one way to change the voltage in a circuit. Each cell adds more energy, so using more cells increases the voltage.
Cells (batteries) are one way to change the voltage in a circuit. Each cell adds more energy, so using more cells increases the voltage.
When the voltage increases:
- a bulb becomes brighter
- a buzzer becomes louder
A circuit with only one cell has less energy, so the effect is smaller. Adding a second or third cell makes a noticeable difference to how the circuit works.
Scientists test this by building circuits with different numbers of cells and carefully comparing the results. To keep the test fair, they change only one thing at a time and observe what happens.
This helps scientists understand how electrical devices are designed to work safely and effectively.
Changing cells
- Build a simple circuit with one cell and a bulb. If you don't have a circuit kit of your own use this website.
- Observe how bright the bulb is.
- Then add another cell and compare the brightness.
- What changes do you notice? Can you explain why this happens?
Understanding how cells affect a circuit helps scientists design electrical devices that work safely and efficiently.
 Circuit simulator
Circuit simulatorExplore series and parallel circuits, test ideas and build your own virtual circuits.
Comparing circuits and components
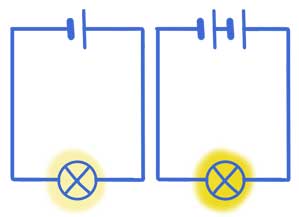 Two circuits can look very similar but work in different ways. Even small changes can make a big difference to how a circuit behaves. Adding an extra cell, changing a component or adjusting a switch can change how electricity moves around the circuit.
Two circuits can look very similar but work in different ways. Even small changes can make a big difference to how a circuit behaves. Adding an extra cell, changing a component or adjusting a switch can change how electricity moves around the circuit.
Different components affect circuits in different ways. For example, bulbs can shine with different levels of brightness, buzzers can produce sounds that are louder or quieter, and switches control when electricity is allowed to flow. Each part has a specific job, and changing one part can affect the whole circuit.
Scientists compare circuits carefully to understand these differences. They build circuits, test them and collect evidence about what happens. To make fair comparisons, they change only one thing at a time and observe how it affects the result.
By comparing circuits and components, scientists can explain why electrical devices work as they do and how to make them work better and more safely.
Switches
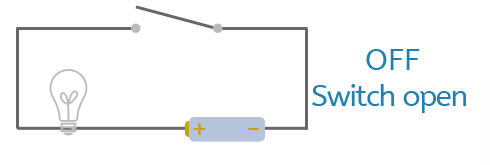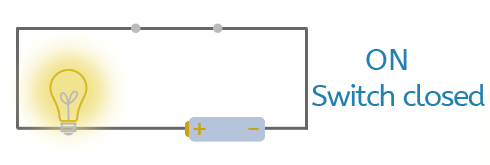
Switches are used to control circuits safely and easily. They allow us to choose when electricity flows and when it stops. Switches are found in homes, machines and technology all around us, such as light switches, toys, appliances and electronic devices.
In a circuit, a switch works by breaking or completing the path that electricity travels around. This gives us control over the circuit without needing to touch the wires or batteries.
A switch breaks the flow of electricity when it is off (open). Opening the switch creates a gap in the circuit so electricity cannot flow.
Closing a switch, (on), completes the circuit. This allows electricity to flow all the way around the circuit, so bulbs light up, or buzzers sound.
Switches help make electrical devices safer, more useful and easier to control. By understanding how switches work, scientists and engineers can design circuits that turn on and off exactly when needed.
Drawing circuits
Scientists do not usually draw circuits as pictures. Instead, they use circuit symbols. Each symbol stands for a different component, such as a cell, bulb, switch or wire. These symbols are recognised everywhere and are used by scientists and engineers around the world.
Using symbols helps make circuit diagrams clear, simple and easy to understand. Anyone who knows the symbols can look at a diagram and understand how the circuit is arranged.
Learning circuit symbols allows you to:
- plan a circuit before building it
- record your work clearly
- share ideas with others
Once you know the symbols, you can draw your own circuits and check whether they match the real ones you build.
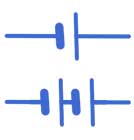
A cell (battery)
A cell provides the energy that pushes electricity around a circuit. Sometimes circuits use more than one cell joined together. When two or more cells are connected, they are called a battery.
Using more cells increases the voltage, giving electricity a stronger push. This can make bulbs shine brighter or buzzers sound louder.
Cells can be drawn in circuit diagrams as one cell or as multiple cells in a row, depending on how many are used in the circuit.
Without cells or batteries, electricity cannot flow and the circuit cannot work.

Wires
Wires connect all the parts of the circuit together. They provide the path that electricity travels along.
Electricity flows through the wires from the cells, through the components, and back to the cells again. If a wire is loose or broken, the circuit will be incomplete and electricity will stop flowing.
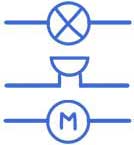
Output components
Output components use electrical energy and change it into other types of energy. In simple circuits, these usually include:
- Bulbs – change electricity into light
- Buzzers – change electricity into sound
- Motors – change electricity into movement
A simple circuit usually includes one output component, but more complex circuits can include several.
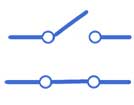
A switch
A switch controls whether electricity can flow around the circuit.
- When the switch is closed (on), it completes the circuit and allows electricity to flow.
- When the switch is open (off), it breaks the circuit and stops electricity from flowing.
Switches allow us to turn devices on and off safely and are used in lights, toys, and many everyday appliances.
Building circuits
Building circuits helps scientists understand how electricity works. By connecting different components and testing what happens, we can learn how circuits behave and how changes affect them.
When building circuits, scientists:
- connect components carefully so electricity can flow
- test whether the circuit works as expected
- identify and fix problems if it does not work
This process requires patience, problem-solving and careful thinking. Scientists often test their ideas many times before getting a circuit to work correctly.
You can explore circuits safely using online circuit-building games. These let you add bulbs, buzzers, switches and batteries to see what happens. Try changing the number of components or adding more cells and observe how the circuit changes.
 Circuit simulator
Circuit simulatorExplore series and parallel circuits, test ideas and build your own virtual circuits.
 Blobz: Electic Circuits
Blobz: Electic CircuitsLearn about circuits, then play the game and take the quiz to test what you know.
 Crack the circuit
Crack the circuitIn this electrical circuit game, use batteries, bulbs and switches to solve the mystery circuit. Learn about series, parallel, short circuits and more.
 Power up: Circuit Builder
Power up: Circuit BuilderDrag the components to where you want them in the circuit. Choose a battery and explore.
Where does electricity come from?
Electricity does not appear by itself. It has to be made. Most of the electricity we use is produced in power stations using special machines called generators.
A generator makes electricity by turning energy from one form into electrical energy. When the generator spins, it creates an electric current that can travel through wires.
Energy sources that make electricity
 Generators need energy to make them turn. This energy can come from different sources, including:
Generators need energy to make them turn. This energy can come from different sources, including:
- Gas, coal or oil – these fuels are burned to create heat, which makes machines spin
- Wind – wind turbines turn when the wind blows
- Solar power – sunlight is changed into electricity using solar panels
- Water – flowing or falling water turns turbines in dams or rivers
Each of these sources provides the energy needed to keep the generator moving.
From power station to plug socket
Once electricity is made, it travels along cables and power lines to reach homes, schools, shops and other buildings. From there, it can be used to power lights, computers, televisions and many other devices we use every day.
Electricity must be produced all the time because it cannot easily be stored in large amounts. This is why power stations are always working to meet our needs.
 BBC Bitesize - What is electricity?
BBC Bitesize - What is electricity?Electricity is created by generators which can be powered by gas, coal, oil, wind or solar.
Electricity can change into other types of energy
Electricity is very useful because it can be changed into different types of energy depending on what a device needs to do. This is why electricity is used in so many appliances around us every day.
When electricity flows through a device, it can be converted into:
- Light – Lamps, bulbs, torches and LED displays turn electrical energy into light so we can see.
- Heat – Kettles, toasters, heaters and ovens change electricity into heat to warm things up or cook food.
- Movement – Fans, washing machines, electric cars and motors use electricity to make things move.
- Sound – Buzzers, speakers, radios and alarms turn electricity into sound to alert, entertain, or communicate.
This ability to change electricity into other forms of energy is what makes it so powerful and useful. By understanding how energy can be converted, scientists and engineers can design devices to do all kinds of work safely and efficiently.
Light, heat or sound?
- Look around your home and find devices that use electricity.
- Can you identify which type of energy each one produces? Is it light, heat, movement, or sound?
Staying safe with electricity
Electricity is extremely useful, but it can also be dangerous if it is not used safely. That is why it is very important to follow safety rules whenever you use electrical devices or appliances. Understanding electricity helps us use it responsibly and carefully.
Here are some important safety rules:
- Never touch electrical equipment with wet hands
Water can carry electricity, so touching plugs or appliances with wet hands can be very dangerous. - Never put objects into sockets
Sockets are designed for plugs only. Sticking other objects inside can cause a shock or start a fire. - Do not use damaged plugs or wires
Worn or broken wires can expose electricity and make it unsafe to use. Always check that cords are in good condition. - Always ask an adult for help
If you are unsure about anything electrical, always get help from a parent, teacher, or adult. They can make sure it is safe to use.
Electricity can give us light, heat, sound, and movement, but it can also harm people if it is used incorrectly. Following safety rules keeps us and others safe while still allowing us to enjoy all the benefits of electricity.








